Our indexes include entries for the spelling harman. In the period you have requested, we have the following 869 records (displaying 11 to 20):
Liegemen and traitors, diplomats and spies
(1540-1542)
The Privy Council of England dealt with many delicate and important matters of state. The surviving records date back as early as the 14th century, but Henry VIII on 10 August 1540, with the advice of the council, ordered that the council should have its own clerk 'to write, entre and registre all such decrees, determinacons, lettres and other such things as he shuld be appoynted to entre in a booke, to remayne alwayes as a leger, aswell for the dischardge of the sayd counsaillours touching such things as they shuld passe from tyme to tyme, as alsoo for a memoriall unto theim of their owne procedings'. The register from that date to 8 April 1542 was transcribed for the Commissioners of the Public Records by sir Harris Nicolas, and published in 1837. Although the council often dealt with petitions from aggrieved subjects, its main function was to oversee internal and external security. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Inhabitants of Calais, and visitors
(1485-1543)
Richard Turpyn, a burgess of Calais, the English enclave on the French coast, compiled (or possessed) a chronicle of events there from 1485 to 1540, a copy of which survived among the Stowe manuscripts in the Harleian collection in the British Museum. This was edited for the Camden Society, together with a number of other papers relating to events in Calais in that period, by John Gough Nichols, and printed in 1846. Many of the persons named in the resulting book are knights and noblemen attending king Henry VII and king Henry VIII when on the Continent on diplomatic or marital business; but there is also a muster roll of the garrison of Calais of 1533 (136-139). | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Liegemen and Traitors, Pirates and Spies
(1542-1547)
The Privy Council of Henry VIII was responsible for internal security in England and Wales, and dealt with all manner of special and urgent matters
| Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Liegemen and Traitors, Pirates and Spies
(1547-1550)
The Privy Council of Edward VI was responsible for internal security in England and Wales, and dealt with all manner of special and urgent matters
| Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Officers of the Royal Household
(1553)
King Edward VI died 6 July 1553 and was buried 8 August following. The accounts of the funeral expenses were prepared by sir Edward Waldegrave, knight, one of queen Mary's privy coucil, and master of her Majesty's great wardrobe. The expenses included the purchase of 'blacke clothe boughte for the buriall' to furnish mourning for every officer and servant of the late king's household, and these accounts list all the officers, department by department, by name. Most officers were provided with 4 yards of cloth, and their clerks and servants 3 yards each: greater dignitaries were allowed from 7 to 16 yards; sir Edward himself received 10. The total cost of the 9,376 and a half yards of cloth was £5946 9s 9d. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Liegemen and Traitors, Pirates and Spies
(1554-1556)
The Privy Council of queen Mary was responsible for internal security in England and Wales, and dealt with all manner of special and urgent matters.
| Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Tradesmen of York
(1272-1558)
No man or woman could trade in the city of York without having obtained 'freedom' of the city.Their names were recorded on the 'Freemen's Roll', or Register of the Freemen of the City of York, which contains about 19,900 names for this period. A list of names was prepared for each year, the year being here reckoned as starting at Michaelmas (29 September) until 1373, and thence at Candlemas (2 February). Each annual list starts with the name of the mayor and the camerarii or chamberlains. The chamberlains were freemen charged with the duty of receiving the fees of the new freemen; of seeing that only freemen traded in the city; and of preparing this roll, which was compiled from the names on their own account books from the receipts for the fees. There are three groups of freemen: those who obtained freedom after serving out an apprenticeship to a freeman; the children of freemen; and those who claimed freedom by 'redemption', i. e. by purchase or gift from the Mayor and Court of Aldermen.
| Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Warwickshire Entries in the Court of King's Bench (1558)
The Coram Rege Chief Justice's Roll for Michaelmas 5 & 6 Philip & Mary and 1 Elizabeth with cases heard at Westminster of litigants from throughout England
| Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Kent clergy
(1560-1562)
Lists of clerks admitted to benefices in Canterbury diocese and jurisdiction, recorded in the register of archbishop Matthew Parker | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
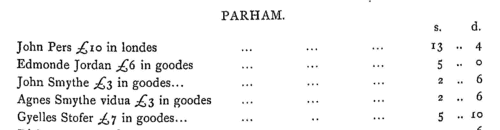
Inhabitants of Suffolk
(1568)
By Act of Parliament of December 1566 a subsidy of 8d in the £ on moveable goods and 4s in the £ on the annual value of land was raised from the lay (as opposed to clergy) population. These are the returns for Suffolk, printed in 1909 in the Suffolk Green Book series. | Sample scan, click to enlarge
|
Research your ancestry, family history, genealogy and one-name study by direct access to original records and archives indexed by surname.











