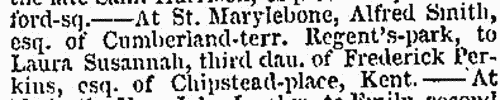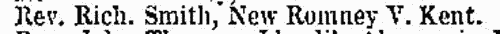Our indexes include entries for the spelling barlow. In the period you have requested, we have the following 1,850 records (displaying 931 to 940):
Bankrupts
(1839)
Bankruptcy notices for England and Wales: bankruptcy often caused people to restart their lives elsewhere, so these are an important source for lost links
| Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Deaths, Marriages, News and Promotions
(1839)
Death notices and obituaries, marriage and birth notices, civil and military promotions, clerical preferments and domestic occurrences, as reported in the Gentleman's Magazine. Mostly from England and Wales, but items from Ireland, Scotland and abroad.
| Sample scan, click to enlarge
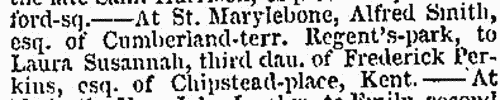
|
Deaths, Marriages, News and Promotions
(1839)
Death notices and obituaries, marriage and birth notices, civil and military promotions, clerical preferments and domestic occurrences, as reported in the Gentleman's Magazine. Mostly from England and Wales, but items from Ireland, Scotland and abroad.
| Sample scan, click to enlarge
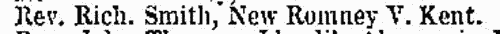
|
Insolvents
(1839)
Insolvency notices for England and Wales: insolvency often caused people to restart their lives elsewhere, so these are an important source for lost links | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Petitioning Creditors and Solicitors
(1839)
Principal creditors petitioning to force a bankruptcy (but often close relatives of the bankrupt helping to protect his assets): and solicitors | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Trustees and Solicitors
(1839)
Trustees appointed to take over bankrupts' estates in England and Wales, and their solicitors. Trustees are often friends or relatives of the bankrupt: and/or principal creditors
| Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
 British merchant seamen
(1835-1840) British merchant seamen
(1835-1840)
At this period, the foreign trade of ships plying to and from the British isles involved about 150,000 men on 15,000 ships; and the coasting trade about a quarter as many more. A large proportion of the seamen on these ships were British subjects, and so liable to be pressed for service in the Royal Navy; but there was no general register by which to identify them, so in 1835 parliament passed a Merchant Seamen's Registration Bill. Under this act a large register of British seamen was compiled, based on ships' crew lists gathered in British and Irish ports, and passed up to the registry in London. A parliamentary committee decided that the system devised did not answer the original problem, and the original register was abandoned after less than two years: the system was then restarted in this form, with a systematic attempt to attribute the seamen's (ticket) numbers, and to record successive voyages. The register records the number assigned to each man; his name; age; birthplace; quality (S = seaman, &c.); and the name and official number of his ship, with the date of the crew list (usually at the end of a voyage). Most of the men recorded were born in the British Isles, but not all. The system was still very cumbersome, because the names were amassed merely under the first two letters of surname; an attempt was made to separate out namesakes by giving the first instance of a name (a), the second (b), and so on. This section of the register (BT 112/2) covers numbers 1 to 2952 and 20200 to 23034, 5786 different entries, of men whose surnames began with the letters Ba. During 1840 this series of ledgers was abandoned, and a new set started with names grouped together by surname. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Bankrupts
(1840)
Bankruptcy notices for England and Wales: bankruptcy often caused people to restart their lives elsewhere, so these are an important source for lost links
| Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Bankrupts
(1840)
Lists of dividends from bankrupts' estates for England and Wales: bankruptcy often caused people to restart their lives elsewhere, so these are an important source for lost links
| Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Boys entering Rugby School
(1840)
This edition of Rugby School Register was published in 1933: the volume covering 1675 to 1857 contains 6480 entries, based on the original school admission registers, but elaborated with general biographical information wherever the editor was able to do so. The entries for the 17th and early 18th centuries are much less detailed than those for later years. The arrangement of the fullest entries was to give the boy's full name (surname first, in bold); whether eldest, second, &c., son; father's name and address as of when the boy entered school; the boy's age at entry and birthday; name of the house (in the school) to which he belonged; then a brief general biography; and date and place of death. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Research your ancestry, family history, genealogy and one-name study by direct access to original records and archives indexed by surname.