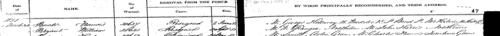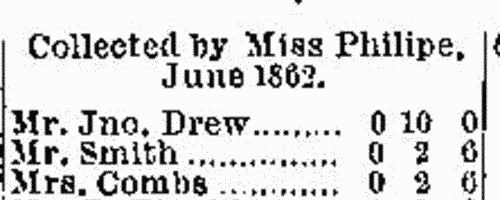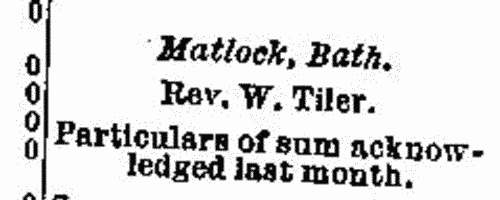Add this eBook to your basket to receive access to all 58 records. Our indexes include entries for the spelling atty. In the period you have requested, we have the following 58 records (displaying 41 to 50): These sample scans are from the original record. You will get scans of the full pages or articles where the surname you searched for has been found. Your web browser may prevent the sample windows from opening; in this case please change your browser settings to allow pop-up windows from this site. Gentry in London
(1856)
The Post Office London Directory for 1856 includes this 'Court Directory', listing alphabetically by surname and christian name the upper class residents of the capital with their postal addresses. 'In order to afford space for the addresses, the abbreviation "esq." for esquire has no longer been appended to each name in the Court Directory. It should be understood that such should be added to the name of every gentleman in the following pages to which no inconsistent addition is affixed.' Decorations, honours &c. are generally given. Some gentlemen appear who are also listed (as professional men, &c.) in the commercial section. Those with second residences in the provinces usually have the country address given as well. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Traders and professionals in London
(1856)
The Post Office London Directory for 1856 includes this 'Commercial and Professional Directory', recording over 100,000 individuals. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|  Persons of standing recommending London police recruits
(1843-1857) Persons of standing recommending London police recruits
(1843-1857)
The Metropolitan Police Register of Joiners (MEPO 4/334) lists policemen joining the force 1 January 1843 to 1 April 1857 (warrant numbers 19893 to 35804). The register is alphabetical, in so far as the recruits are listed chronologically grouped under first letter of surname. It gives Date of Appointment, Name, Number of Warrant, Cause of Removal from Force (resigned, dismissed, promoted or died), and Date of Removal. Although the register was closed for new entrants at the end of 1842, the details of removals were always recorded, some being twenty or more years later. Those recruits not formerly in the police, the army, or some government department, were required to provide (normally) at least two letters of recommendation from persons of standing, and details of these are entered on the facing pages. Where a recruit was only recently arrived in the metropolis, the names and addresses of the recommenders can be invaluable for tracing where he came from. Those recruits not formerly in the police, the army, or some government department, were required to provide (normally) at least two letters of recommendation from persons of standing, and details of these are entered on the facing pages: the names in these are indexed here (the police recruits are indexed separately and not included here). Recruits transferred from other forces or rejoining the force did not normally need recommendations - in the latter case, former warrant numbers are given - but some recommendations are from police inspectors, even other constables. Recruits coming from the army sometimes have general military certificates of good conduct, but most often have a letter from their former commanding officer; recruits recommended by government departments (most often the Home Office) similarly have letters from the head of department. But the great majority of the names and addresses in these pages are of respectable citizens having some sort of personal acquaintance with the recruit. Where more than two recommendations were provided, the clerk would only record one or two, with the words 'and others'. Tradesmen are sometimes identified as such by their occupations; there are some gentry. Although the bulk of these names are from London and the home counties, a scattering are from further afield throughout Britain and Ireland. | Sample scan, click to enlarge
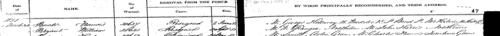
| Officers of the British Army
(1860)
The New Annual Army List first lists officers of the rank of major and above, by rank, and with dates of appointment to each successive higher rank, and (where appropriate) when placed on half pay. An asterisk indicates temporary rank; a superscript p shows that a commission was purchased; a dagger shows officers on the half pay of their last regimental commission. An ornate W indicates those officers actually present in any of the actions of 16, 17 or 18 June 1815 and therefore awarded the Waterloo Medal; P is put before the name of an officer who served in the Peninsula or the South of France; T for the Battle of Trafalgar; VC for the Victoria Cross. For each officer in this section, the final column notes his then present or immediately former regiment and/or office, if any. Next, all the officers of the army are listed, down to the rank of ensign, by regiment or corps, giving rank, name, date of rank in the regiment, and date of rank in the army, with occasional further notes. Again, holders of medals are duly noted, as in the first list. For each regiment the paymaster, adjutant, quartermaster, surgeon and assistant surgeons are named, as well as the civilian agent; and the regimental motto, battle honours, and colours of the facings and lace of the dress uniform are stated. After the British regiments of the line, the Rifle Brigade, the officers of the West India infantry, the Ceylon rifles, the Cape Mounted Riflemen, the Royal Canadian Rifles, St Helena Regiment and the Gold Coast Artillery Corps are given; then the officers of the garrisons and other military establishments; the Royal Artillery; Royal Engineers; Royal Marines; Commissariat Department; Medical Department; Staff Officers of Pensioners; Chaplains' Department; Staff (of Great Britain, Australia, Bahamas, Bermuda, British Columbia, Cape of Good Hope, Ceylon, East Indies, Falkland Islands, Gibraltar, Heligoland, Hong Kong, Ionian Islands, Jamaica (including Honduras), Malta, Mauritius, Newfoundland, North America, St Helena, the Western Coast of Africa, and the Windward and Leeward Islands); Military and Civil Department; and Barrack Masters. Then there is a separate list of officers retained on retired full pay and half pay (including the German Legion, the Brunswick Cavalry, the Brunswick Infantry, Chasseurs Brittaniques, Royal Corsican Rangers, the Greek Light Infantry, Royal Malta Regiment, Meuron's Regiment, Roll's Regiment, Sicilian Regiment, Watteville's Regiment, the York Light Infantry Volunteers, Foreign Veteran Battalion and the Foreign Corps of Waggoners). | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Missionaries and contributors
(1863)
The Evangelical Magazine and Missionary Chronicle records the work of Christian missionaries throughout the world, and of the supporting missionary societies collecting money for the work in the British Isles. Contributions are listed by congregation, and by family members making donations. | Sample scan, click to enlarge
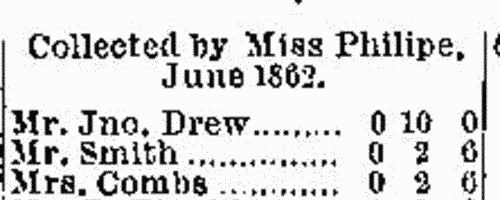
| Missionaries and contributors
(1864)
The Evangelical Magazine and Missionary Chronicle records the work of Christian missionaries throughout the world, and of the supporting missionary societies collecting money for the work in the British Isles. Contributions are listed by congregation, and by family members making donations. | Sample scan, click to enlarge
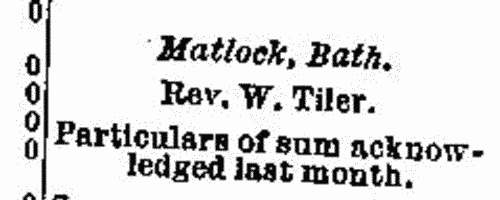
| Pupil Teachers training to become masters in Elementary Schools
(1875)
The Education Department set examinations for candidates for admission into training colleges, and to become teachers. This is the class list (in order of merit) of the men who took the examination to become masters in elementary schools at Christmas 1875. The candidates' names are listed alphabetically by surname within each division, with school in which engaged (N. for National School, Ch. Church of England, B. British School, W. Wesleyan, R. Roman Catholic, P. Parochial, Bd. Board School, Indl. Industrial School). (The sample scan is from a general class list for schoolmistresses) | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Baptists
(1876)
The Baptist was a weekly newspaper, with some general news and political coverage, but mainly devoted to chronicling Denominational Intelligence, i. e. the doings of the Baptist churches in Britain and Ireland. January to June 1876. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Missing Next-of-Kin and Heirs-at-Law
(1880)
The Unclaimed Money Registry and Next-of-Kin Advertisement Office of F. H. Dougal & Co., on the Strand in London, published a comprehensive 'Index to Advertisements for Next of Kin, Heirs at Law, Legatees, &c., &c., who have been Advertised for to Claim Money and Property in Great Britain and all Parts of the World; also Annuitants, Shareholders, Intestates, Testators, Missing Friends, Creditors or their Representatives, Claimants, Unclaimed and Reclaimed Dividends and Stock, Citations, Administrations, Rewards for Certificates, Wills, Advertisements, &c., Claims, Unclaimed Balances, Packages, Addresses, Parish Clerks' Notices, Foreign Intestates, &c., &c.' The original list was compiled about 1860, but from materials dating back even into the 18th century: most of the references belong to 1850 to 1880. For each entry only a name is given, sometimes with a placename added in brackets: there may be a reference number, but there is no key by which the original advertisement may be traced. The enquirer of the time had to remit £1 for a 'Full and Authentic Copy of the Original Advertisement, together with name and date of newspaper in which the same appeared'. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Debtors, Insolvents and Bankrupts
(1882)
Bills of sale (binding assets to a creditor/lender), insolvencies and bankruptcies in England and Wales, July to September 1882 | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Research your ancestry, family history, genealogy and one-name study by direct access to original records and archives indexed by surname.
|