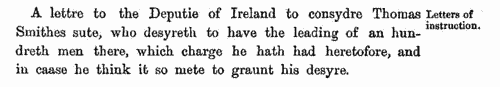Bocher Surname Ancestry ResultsOur indexes 1000-1999 include entries for the spelling 'bocher'. In the period you have requested, we have the following 70 records (displaying 31 to 40): Single Surname Subscription | | | Buying all 70 results of this search individually would cost £360.00. But you can have free access to all 70 records for a year, to view, to save and print, for £100. Save £260.00. More... |
These sample scans are from the original record. You will get scans of the full pages or articles where the surname you searched for has been found. Your web browser may prevent the sample windows from opening; in this case please change your browser settings to allow pop-up windows from this site. Taxpayers in Sussex
(1524-1525)
By Act of Parliament of 1523 (14 & 15 Hen. III, c. 16) a general subsidy was raised, spread over four years, from laymen, clergy and peers. In each of the first two years 1s in the £ was raised from annual income from land; 1s in the £ on capital goods worth over £2 and under £20; and a flat payment of 4d on goods worth from £1 to £2, and also by persons aged 16 and upwards in receipt of £1 per annum in wages. In the third year a further shilling in the pound was payable on land worth £50 and upwards a year; and in the fourth year a shilling in the pound on goods worth £50 and upwards. To raise this revenue, returns were required from every hundred, parish or township. In Sussex, the returns for 1524 and 1525 cover the city of Chichester (divided into Estrata, Westrata, Southstrata, North[strata] and Palenta), the borough of Midhurst, and then the rest of the county divided into rapes, within those into hundreds, and within those into boroughs, tithings, liberties, townships or parishes. It is important to note that the cinque ports of Hastings, Rye and Winchelsea were exempt from the subsidy, except for alien inhabitants; and that the town of Westbourne was also exempted 'as the town was lately destroyed by fire'. Aliens are noted as such, sometimes with nationality; and Brighthelmstone (Brighton), which had been burnt by the French in 1514, is only represented fragmentarily. The Sussex Record Society published this transcript and edition by Julian Cornwall of the 1524 and 1525 returns: the 1524 return was used for the main transcript where possible, names peculiar to the 1524 lists being marked with an asterisk, and those with amendments in 1524 with a dagger. At the foot of each 1524 return the new names from 1525 are given. Only the amount of the assessment is printed (m. = marks). Letters prefixed to the sum give the basis of the assessment, no letter (or G) meaning that it was on goods - A, annual wages; D, annual wages of day-labourers; F, fees or salaries of office; L, lands; P, profits; W, wages; x, no basis stated. BOCHER. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge
| Somerset testators and legatees
(1501-1530)
Somerset was almost coextensive with the diocese of Bath and Wells, which exercised local probate jurisdiction through its consistory and archdeaconry courts: but superior to the diocese was the province of Canterbury. Somerset testators who also had property outside the county had their wills proved in the Prerogative Court of Canterbury (PCC). The Somerset Record Society embarked on a program of publishing genealogical abstracts of the registered copy wills of Somerset testators in the PCC archives, and in 1903 (volume xvi) printed abstracts edited by the Reverend F. W. Weaver from the PCC registers 1501-1503 (register Blamyr), 1504-1506 (Holgrave), 1506-1508 (Adeane), 1508-1511 (Bennett), 1511-1514 (Fetiplace), 1514-1517 (Holder), 1517-1520 (Ayloffe), 1520-1522 (Maynwaryng), 1523-1525 (Bodfelde), 1525-1528 (Porch) and 1529-1530 (Jankyn). In addition, the volume includes abstracts of 48 Somerset copy wills in the registers of the Archbishops of Canterbury at Lambeth Palace Library from 1363 to 1491. The heading of each abstract gives the year of making the will (not the year of probate) and the testator's name in bold. Below that is the quire number and name of the PCC register. Date and details of probate are given at the foot of each abstract. Spellings of surnames are preserved as they appear in the registered copy wills, and may vary within a single document.BOCHER. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Inhabitants of Stratford upon Avon in Warwickshire
(1406-1535)
The Hospital of the Holy Cross was founded in 1269; in time this fraternity became a social and religious gild. 'The Register of the Gild of the Holy Cross, the Blessed Mary and St John the Baptist of Stratford-upon-Avon' was edited by J. Harvey Bloom, rector of Whitchurch, and printed in 1907. The register is a record of admissions to the gild, an account of the fines paid by new members, and the names of those in arrear. Each year's record usually starts on the Monday after Ascension Day (the sixth Thursday after Easter), when the new aldermen, master and proctors of the gild were elected, all duly named. Then follow the admissions to the gild, including payments for prayers and candles (lights) for the faithful dead; and the names of the sureties for these payments. Interspersed with this are occasional proclamations and memoranda concerning the fraternity. A peculiarity of this publication is that the years given at the head of each page (e. g. 1502-3) are those of the regnal year (in that case 18 Henry VII) in which the Monday after Ascension Day fell. The regnal years of Henry IV, Henry VI, Richard III and Henry VII all started after that day in the calendars of 1399, 1422, 1483 and 1485; so the gild registers during those years actually cover the following year to that shown in this printed text (in that case, 1503-4).
BOCHER. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Murderers sheltering in Beverley Minster: and their victims
(1478-1539)
Criminals could evade pursuit by claiming sanctuary in the church of St John in Beverley, in the East Riding of Yorkshire. This liberty of the minster extended a league in every direction from the church door, and was divided into six sections, each giving greater sanctity to the rights of sanctuary, the sixth and innermost section being the presbitery or chancel. Near the altar there was a stone chair called the Frith Stool, seated on which an accused could claim total immunity. The bailiff would receive the oath of the fugitive, and a clerk recorded 'what man he killed, and wher with, and both ther namez'; the bailiff receiving a fee of 2s 4d, the clerk 4d. Sanctuary was afforded for 30 days, with food and lodging, after which the fugitive was protected to the borders of the county. But within 40 days he had to appear before the coroner, clothed in sackcloth, and be branded on his right hand with the sign of the letter A. This signified that he was swearing to abjure the realm: he was then free to leave the country unhindered. At Beverley the clerks kept a separate register of fugitives' petitions, which survives from 1478 to 1539 in Harleian Manuscript 560. It was edited and printed by the Surtees Society in 1837 under the title Sanctuarium Beverlacense. Some of the criminals came from a considerable distance: the great majority were murderers or homicides. Each entry usually gives full name, original address, (often) trade, a brief description of the crime, often with date, and usually the name of the victim. This index covers all the surnames given.BOCHER. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Garforth Archers
(1539)
In anticipation of war with France, Henry VIII ordered a general muster of able-bodied men throughout the kingdom. That for the wapentake of Skyrack, in the West Riding of Yorkshire, took place at Wike (near Leeds) before sir William Gascoigne the elder, sir William Middleton and sir William Maleverer, on 26 March 1539. Skyrack wapentake consisted of the ancient parishes of Aberford, Adel, Bardsey, Barwick in Elmet, Bingley, Collingham, Garforth, Guiseley, Harewood, (part of) Ilkley, Kippax, Otley, Swillington and Thorner, as well as the borough of Leeds. This muster roll listing the archers, billmen and spearmen of the wapentake by township or constablewick, was preserved among the State Papers in the Public Record Office; it was edited by W. Paley Baildon, and printed in three issues of the Miscellanea of the Thoresby Society (volumes 4 and 9) through to 1899. For each township there is a list of archers, divided into those fully and those partly ('parcel') armoured ('harnessed'), and a similar list of billmen; a few spearmen also appear. The weapon of the billmen - the bill or halberd - was a blade with a long wooden handle, sometimes with a hook with a cutting edge added at one side.
BOCHER. Cost: £6.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Inhabitants of Nottingham
(1485-1547)
The muniments of the borough of Nottingham include extensive mediaeval archives. A selection from these from the reigns of Henry VII and Henry VIII was prepared and edited by W. H. Stevenson for the Corporation, and printed, with translations of the passages in Latin, in 1885. The principal sources used are the borough Court Books, largely dealing with civil cases, for which an almost complete series survives for this period; Sessions Rolls (92 survive for the two reigns), in which crimes and misdemeanours are recorded; a Mickletorn or Leet jury roll; detailed chamberlains' and bridge-wardens' accounts; and the Hall Books, or council minutes. There are lists of burgesses enrolled; bakers admitted to bake; and fines for licences to trade. A subsidy roll of 1523-4 lists householders by street, and there is an appendix of local deeds, including some material dating back to the 14th century. BOCHER. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Tenants of Somerset chantries
(1548)
Chantries were established to perform services for the souls of their founders and other faithful dead, including annual obits and anniversaries at which alms were usually distributed. The chantries could be at an existing altar in a parish church, a new altar in a side chapel of an existing church, in a new chapel in the churchyard or some miles from an existing church: few were founded before 1300, and most date from 1450 to 1500. Hospitals were places provided by similar foundations to receive the poor and weak; there were also religious guilds, brotherhoods and fraternities, and colleges (like large chantries at which three or more secular priests lived in common). An Act of Parliament of 1545 gave king Henry VIII the power to dissolve such chantries, chapels, &c., the proceeds to be devoted to the expenses of the wars in France and Scotland. Commissioners were appointed 14 February 1546 to survey the chantries and seize their property, and in 1548 the commissioners in Somerset produced this survey and rental. The individuals named are the tenants whose rents provided the chantry's income: occasionally an incumbent is named. The survey was edited by Emanuel Green for the Somerset Record Society, and published in 1888.BOCHER. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Liegemen and Traitors, Pirates and Spies
(1550-1552)
The Privy Council of Edward VI was responsible for internal security in England and Wales, and dealt with all manner of special and urgent matters
BOCHER. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge
| Ludlow Guild: Tenants in Ludlow
(1552)
The Fraternity or Guild of Palmers, founded in Ludlow, Shropshire, possessed extensive property in Ludlow itself and nearby. This survey, taken in the 6th year of king Edward VI, surviving in the records of the Court of Augmentations, lists the tenants of property in Ludlow and its liberties; those of the burgages in Ludlow; of 'divers tenements or burgages, greatly in ruins' with a nominal value of £2 11s 8d per annum, but 'totally in decay', worth 3s 4d for the soil; the sock rents; and various tenements in Ludlow and elsewhere in Shropshire; in Herefordshire; and in Worcestershire.BOCHER. Cost: £6.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Ludlow Guild: Tenants of Ludlow Burgages
(1552)
The Fraternity or Guild of Palmers, founded in Ludlow, Shropshire, possessed extensive property in Ludlow itself and nearby. This survey, taken in the 6th year of king Edward VI, surviving in the records of the Court of Augmentations, lists the tenants of property in Ludlow and its liberties; those of the burgages in Ludlow; of 'divers tenements or burgages, greatly in ruins' with a nominal value of £2 11s 8d per annum, but 'totally in decay', worth 3s 4d for the soil; the sock rents; and various tenements in Ludlow and elsewhere in Shropshire; in Herefordshire; and in Worcestershire.BOCHER. Cost: £6.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Research your ancestry, family history, genealogy and one-name study by direct access to original records and archives indexed by surname.
|