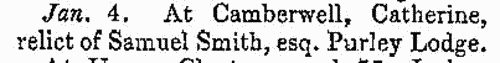Add this eBook to your basket to receive access to all 155 records. Our indexes include entries for the spelling fordyce. In the period you have requested, we have the following 155 records (displaying 81 to 90): These sample scans are from the original record. You will get scans of the full pages or articles where the surname you searched for has been found. Your web browser may prevent the sample windows from opening; in this case please change your browser settings to allow pop-up windows from this site. Bankrupts in England and Wales
(1846)
Perry's Bankrupt and Insolvent Gazette, issued monthly, included lists of bankruptcies and stages in the liquidation of the estate, payment of dividends, and discharge. The initial entry in this sequence gives the name of the bankrupt (surname first, in capitals), the date gazetted, address and trade (often with the phrase dlr. and ch., meaning dealer and chapman); the dates and times and courts of the official processes of surrender; the surname of the official commissioner (Com.); the surname of the official assignee; and the names and addresses of the solicitors; the date of the fiat; and whether on the bankrupt's own petition, or at the demand of petitioning creditors, whose names, trades and addresses are given. In subsequent entries the bankrupt is often merely referred to by name and trade. This is the index to the names of the bankrupts, from the issues from January to December 1846, which may or may not include the detailed first entry for any particular individual. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Bankrupts in England and Wales petitioning for discharge
(1846)
Perry's Bankrupt and Insolvent Gazette, issued monthly, included lists of bankruptcies and stages in the liquidation of the estate, payment of dividends, and discharge. Towards the end of the process there was a Meeting for Allowance of Certificates, where the bankrupt applied for a certificate of discharge. This meeting sometimes took place many years after the bankruptcy procedure started: the details given are the year originally gazetted, name (surname first), address, and trade; and the date and time of the hearing. This is the index to the names of the bankrupts, from the issues from January to December 1846. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Dissolutions of partnerships in England and Wales
(1846)
Perry's Bankrupt and Insolvent Gazette, issued monthly, included lists of dissolutions of partnerships gazetted in England and Wales. The names of the partners are given in full, surnames in capitals, followed by trade and address, and date of the end of the partnership. Each entry usually ends with the phrase 'Debts by ...', indicating which partner intended to continue, and resume the responsibilities of, the business. This is the index to the names of the partners, from the issues from January to December 1846. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| The Edinburgh Gazette
(1846)
The Edinburgh Gazette is the official publication in which various Scottish legal notices are issued, as well as promotions and casualty lists for the British army as a whole, and brief lists of English bankrupts. The key source for tracing details of Scottish bankruptcies, insolvencies, and dissolutions of business partnerships. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Registered Electors of St Cyrus, Kincardineshire (1847)
This alphabetical list gives full names and addresses.
| Sample scan, click to enlarge

| British Army officers in the annexation of the Punjab
(1845-1849)
By 1845 the Sikh state of Lahore was the remaining substantial military power in the Indian sub-continent outside British rule. Its khalsa army was well equipped, disciplined, tenacious and had three European officers among its commanders. The sikhs controlled not only the Punjab, but Pathan tribes as far as the border with Afghanistan, and the whole of Kashmir. The river Sutlej formed the boundary between the Sikh state and British India. In early December 1845 the Sikh army crossed the Sutlej and invested the British garrisons at Ferozepore; 13 December 1845 the British declared war. After defeat in a series of battles, at Moodkee (18-21 December), Ferozeshah (21-22 December); Budhowal and Aliwal (23 December, 28 January); and Sobraon (10 February 1846), the state of Lahore submitted to the Treaty of Lahore, ceding the Punjab between the Sutlej and the Beas, Kashmir, and paying half a crore of rupees. The state of Lahore itself continued under the durbar as a British protectorate during the minority of the young maharajah; and the Sikh army was put under British command. Kashmir was sold by the British to the ruler of Jammu for a crore, and the submission of Kashmir to Jammu was effected by a Sikh force under British officers. British garrisons were placed in the Punjab, but the fort at Multan refused to submit, and had to be besieged. During the siege a Sikh regiment defected to join other khalsa remnants, in defiance of the durbar at Lahore, and raised a rebellion (August 1848 to January 1849). Battles at Chillianwalla (13 January 1849) and Gujerat (21 February 1849) destroyed the Sikh army. The British then annexed the whole of the Punjab, incorporating it into British India. This account of the Annexation of Punjab by Arthur D. Innes and General Charles Gough was published in 1897, but with a poor index; we have remedied that. The account also includes a description of the battles of Maharajapore and Puniar (29 December 1843) by which the army of Gwalior was destroyed. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Bankrupts in England and Wales
(1849)
Perry's Bankrupt and Insolvent Gazette, issued monthly, included lists of bankruptcies and stages in the liquidation of the estate, payment of dividends, and discharge. The initial entry in this sequence gives the name of the bankrupt (surname first, in capitals), the date gazetted, address and trade (often with the phrase dlr. and ch., meaning dealer and chapman); the dates and times and courts of the official processes of surrender; the surname of the official commissioner (Com.); the surname of the official assignee; and the names and addresses of the solicitors; the date of the fiat; and whether on the bankrupt's own petition, or at the demand of petitioning creditors, whose names, trades and addresses are given. In subsequent entries the bankrupt is often merely referred to by name and trade. This is the index to the names of the bankrupts, from the issues from January to December 1849, which may or may not include the detailed first entry for any particular individual. | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Deaths, Marriages, News and Promotions
(1850)
Death notices and obituaries, marriage and birth notices, civil and military promotions, clerical preferments and domestic occurrences, as reported in the Gentleman's Magazine. Mostly from England and Wales, but items from Ireland, Scotland and abroad.
| Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Deaths, Marriages, News and Promotions
(1851)
Death notices and obituaries, marriage and birth notices, civil and military promotions, clerical preferments and domestic occurrences, as reported in the Gentleman's Magazine. Mostly from England and Wales, but items from Ireland, Scotland and abroad.
| Sample scan, click to enlarge
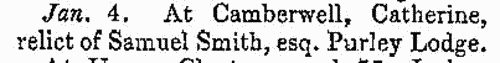
| Pupil Teachers in Yorkshire: Girls
(1851)
The Committee of Council on Education awarded annual grants for the training and support of pupil teachers and stipendiary monitors in schools in England, Wales, Scotland, the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. Pupil teachers started training between the ages of 13 and 15, and 'must not be subject to any bodily infirmity likely to impair their usefulness as Pupil Teachers, such as scrofula, fits, asthma, deafness, great imperfections in the sight or voice, the loss of an eye from constitutional disease, or the loss of an arm or leg, or the permanent disability of either arm or leg, curvature of the spine, or a hereditary tendency to insanity'.
They also had to obtain certificates from the managers of the school (and their clergyman, in the case of Church of England schools) as to their moral character and that of their family; good conduct; punctuality, diligence, obedience, and attention to duty; and attentiveness to their religious duties.
This detailed statement in the annual report of the committee for the year ending 31 October 1851 lists schools by county, giving:
1. Name and Denomination of School, with these abbreviations - B, British and Foreign School Society; F. C., Free Church of Scotland; H. C., Home and Colonial School Society; N., National Society, or connected with the Church of England; R. C., Roman Catholic Poor-School Committee; Wesn., Wesleyan Methodist.
2. Annual grants conditionally awarded by the committee in augmentation of teachers' salaries, and in stipends to apprentices, and gratuities to teachers.
3. Month in which annual examination was to be held.
4. Names of apprentices, giving surname and initials, and year of apprenticeship. Stipendiary monitors are indicated by (S. M.). | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Research your ancestry, family history, genealogy and one-name study by direct access to original records and archives indexed by surname.
|